Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
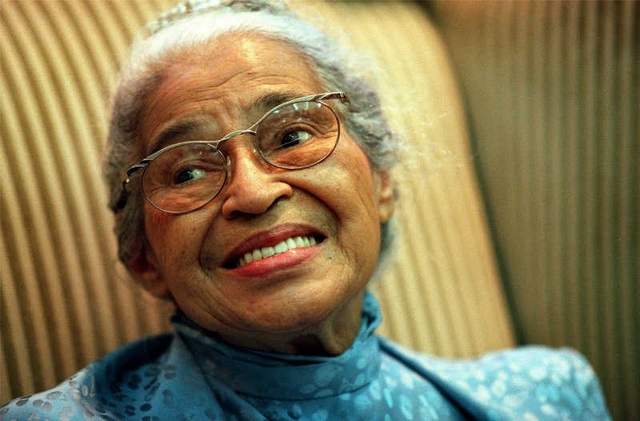 |  |
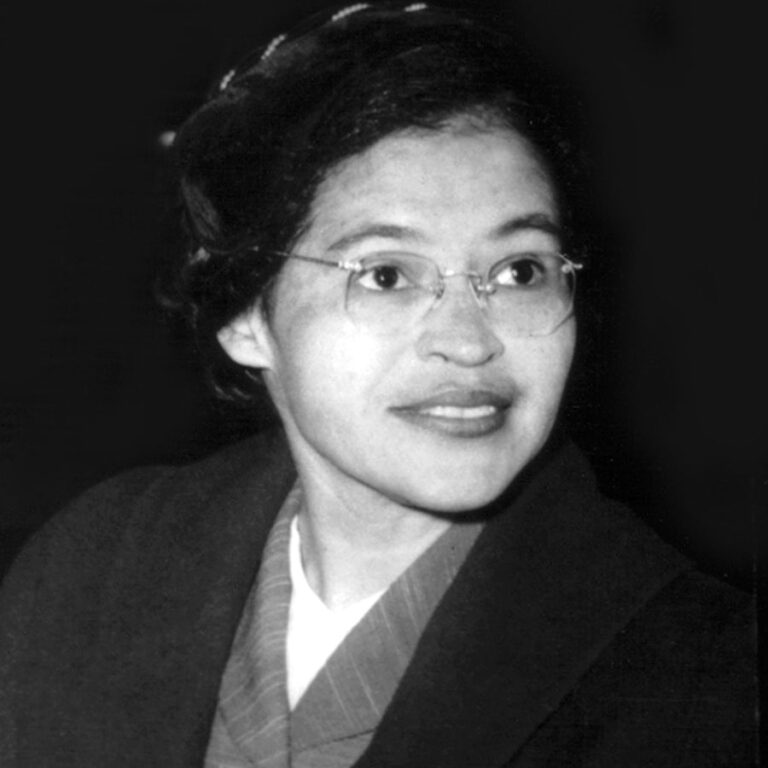
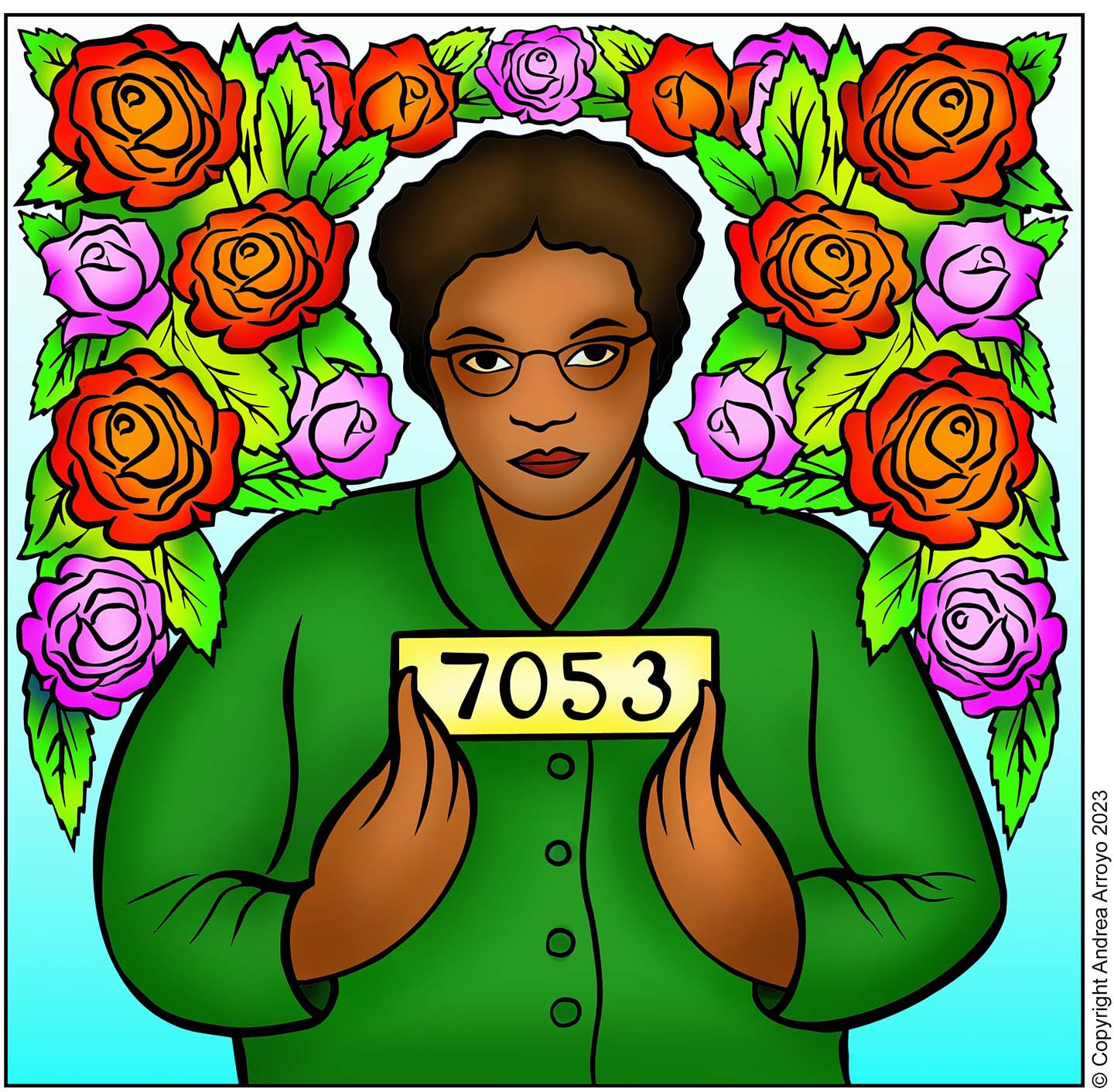
Rosa Parks, born Rosa Louise McCauley on February 4, 1913, in Tuskegee, Alabama, is celebrated as a pivotal figure in the American civil rights movement. Her most notable act of defiance occurred on December 1, 1955, when she refused to yield her bus seat to a white passenger in Montgomery, Alabama. When Rosa passed away on October 24, 2005, at the age of 92, people around the world mourned her loss. Her body lay in honor in the U.S. Capitol Rotunda, an honor reserved for only a few great Americans. Why Rosa Parks Matters. Rosa Parks’ story is a reminder that courage doesn’t always come with loud speeches or grand gestures. The name Rosa Parks is synonymous with courage and defiance in the face of oppression. Her act of refusing to give up her seat on a Montgomery, Alabama bus to a white person on December 1, 1955, sparked the Montgomery Bus Boycott, a pivotal event in the Civil Rights Movement. However, there is more to Rosa Parks than this singular act of bravery. Rosa Parks’ legacy is often simplified to her role in sparking the Montgomery Bus Boycott, but her lifelong commitment to justice went far beyond that single act of defiance. She understood that systemic oppression operates on multiple fronts —racial, gendered, and economic—and that true justice requires addressing all these dimensions. 02/03/2025 February 3, 2025. She stood up for her rights by staying seated. In the 1950s, Rosa Parks gave the US Civil Rights Movement a huge boost, and inspired Martin Luther King Jr. “To reckon with Rosa Parks, the lifelong rebel, moves us beyond the popular narrative of the movement’s happy ending with the passage of the Civil Rights Act and Voting Rights Act to the long and continuing history of racial injustice in schools, policing, jobs, and housing in the United States and the wish Parks left us with—to keep on Rosa Parks (1913—2005) helped initiate the civil rights movement in the United States when she refused to give up her seat to a white man on a Montgomery, Alabama bus in 1955. Her actions By refusing to give up her seat on a segregated bus, Rosa Parks is known as “the mother of the Civil Rights Movement.” Her decision sparked campaigns around the country, which eventually led to the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and Voting Rights Act of 1965. Born in February 1913, Rosa Parks was a civil rights activist whose refusal to give up her seat to a white passenger on a segregated bus in 1955 led to the Montgomery Bus Boycott. Her bravery On 1 December 1955 Rosa Parks was arrested in Montgomery, Alabama, for refusing to give her bus seat to a white passenger. In these exclusive BBC clips, discover how her courageous act of Spread the love En 2013, le mouvement des droits civiques des années 50 aux Etats-Unis revient dans le corps de celui du Black Lives Matter en réponse au meurtre de l’afro-américain Trayvon Martin. Un énième scénario où la vie et les droits du noir sont inexistants en matière d’importance. Où la justice n’est qu’un [] Rosa Parks a terminé ses études secondaires en 1933 avec le soutien de son mari, tout en travaillant également comme couturière. De plus, elle s'est impliquée dans les activités de son mari, qui a collecté de l'argent pour soutenir la défense d'un groupe de Noirs qui avait été faussement accusé d'avoir violé deux femmes blanches. It connects Rosa Parks’s actions to current social justice movements. Ideal for civil rights anniversaries, leadership conferences, and educational events. #3 A Legacy That Lives On. Honored guests and fellow citizens, today we celebrate the enduring legacy of Rosa Parks, a woman whose quiet strength changed America. How Did Rosa Parks’ Actions Influence Legal Proceedings and Changes in Legislation? Rosa Parks’ brave act of not giving up her seat on a bus to a white person challenged the rules that separated black and white people. This led to a big court case, and the judges decided that these separation laws were not allowed by the Constitution. 4. Challenged segregation laws through legal action. Rosa Parks’ refusal to give up her bus seat led to her arrest and subsequent legal challenge to segregation laws in Alabama. The case, known as Browder v. Gayle, was filed by several activists, including Rosa Parks. Rosa Parks (born February 4, 1913, Tuskegee, Alabama, U.S.—died October 24, 2005, Detroit, Michigan) was an American civil rights activist whose refusal to relinquish her seat on a public bus precipitated the 1955–56 Montgomery bus boycott in Alabama, which became the spark that ignited the civil rights movement in the United States. En attendant l’officialisation de l’ouverture en présence de nombreux élus à 15 h, la journée sera également rythmée par la présentation des services et actions proposées par l’Espace social mais aussi par de nombreuses animations culturelles ou festives en mettant en avant des associations locales : projection du court-métrage Instadrame réalisé par les jeunes du CLAS et l Parks fought for her rights and in doing so, paved the way for countless others. Aspire to actions that contribute to collective freedom and equality. 4. “I believe there is only one race – the human race.” Parks emphasized unity over division, reminding us that despite apparent differences, we are fundamentally the same. What were the consequences of Rosa Parks’s actions? After her arrest, Parks faced threats and harassment, leading her to relocate to Detroit. However, her actions also galvanized the African American community and led to significant progress in the civil rights movement. Rosa Parks (center, in dark coat and hat) rides a bus at the end of the Montgomery Bus Boycott, Montgomery, Alabama, Dec. 26, 1956. Don Cravens/The LIFE Images Collection via Getty Images/Getty Images. Most of us know Rosa Parks as the African American woman who quietly, but firmly, refused to give up her bus seat to a white person Dec. 1, 1955, in Montgomery, Alabama. That small act of
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |