Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
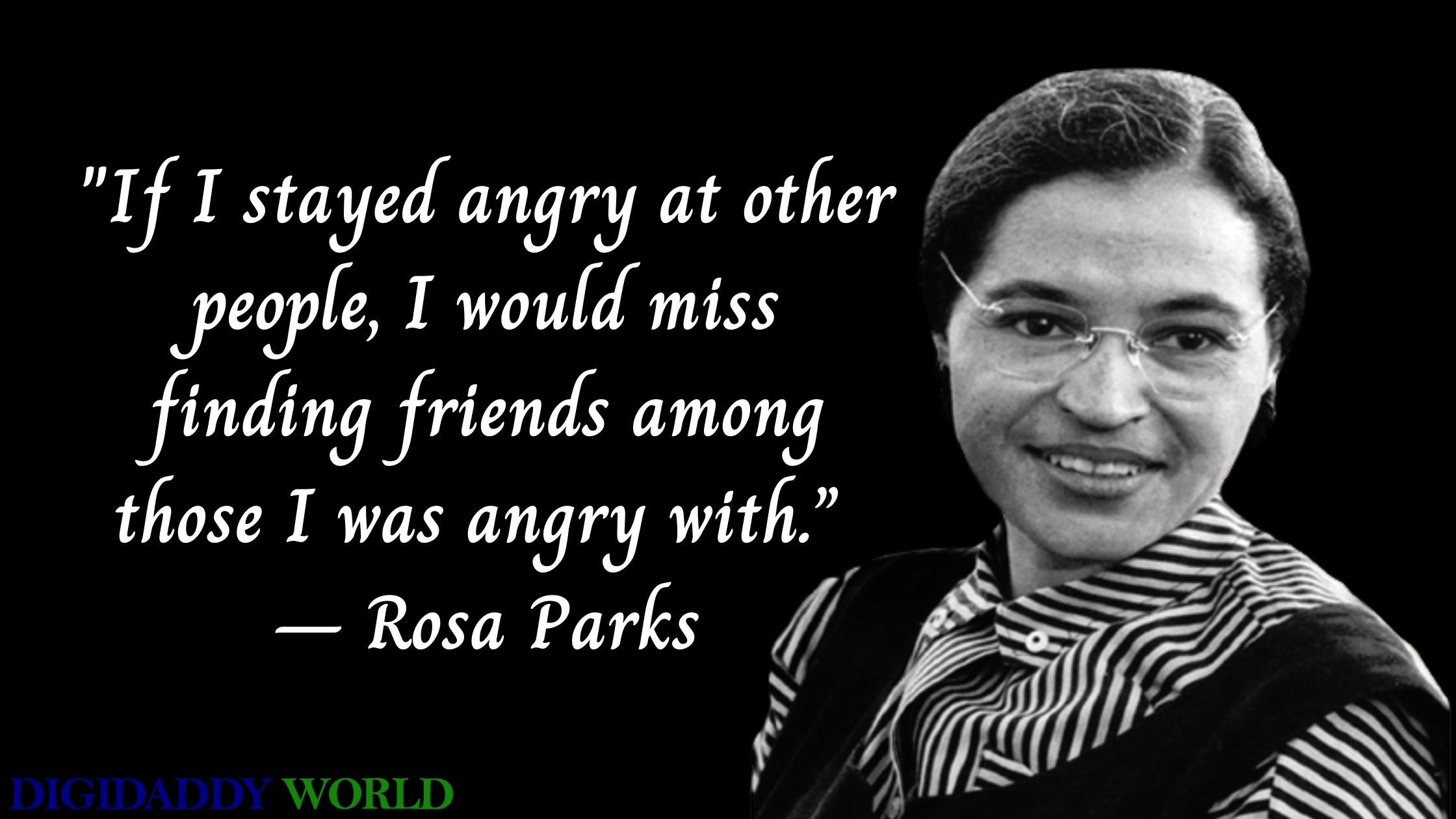 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |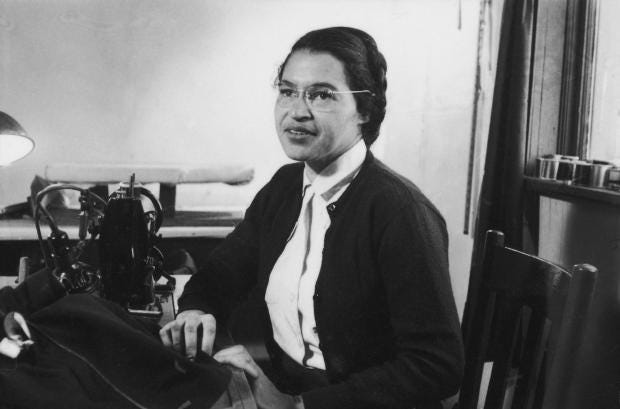  |
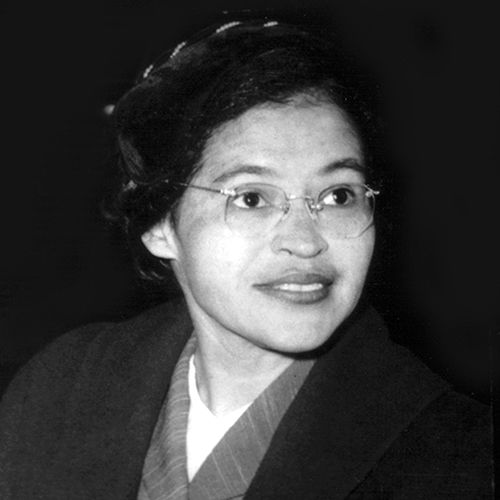
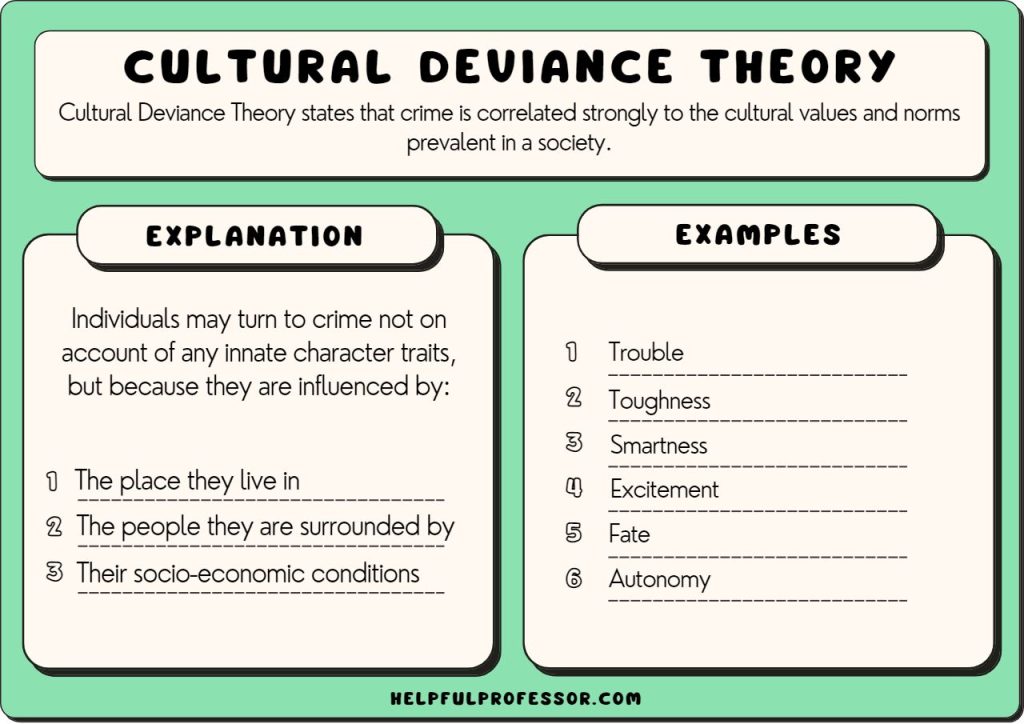
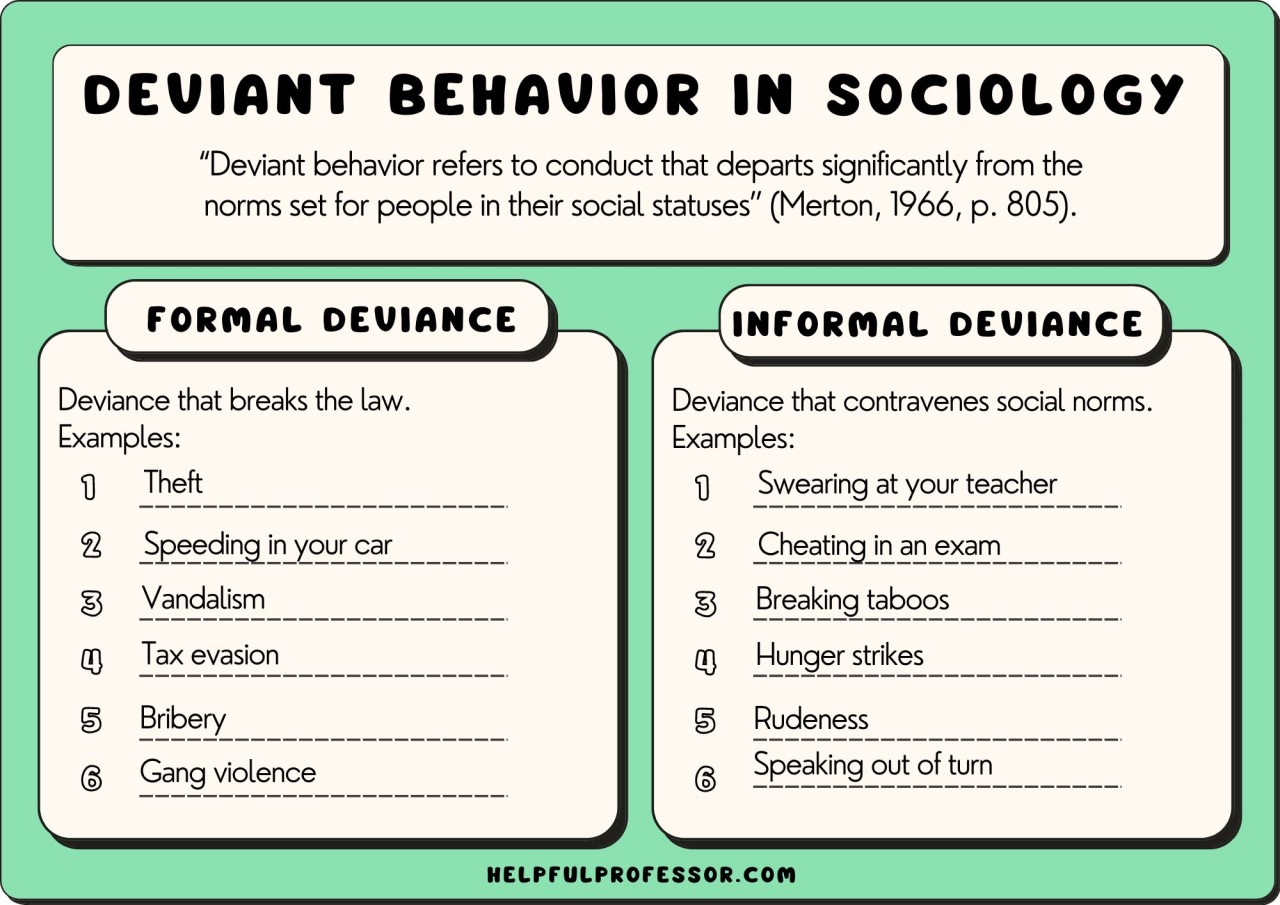
Who is Rosa Parks? Rosa Parks, born Rosa Louise McCauley on February 4, 1913, in Tuskegee, Alabama, is celebrated as a pivotal figure in the American civil rights movement. Her most notable act of defiance occurred on December 1, 1955, when she refused to yield her bus seat to a white passenger in Montgomery, Alabama. Rosa Parks (1913—2005) helped initiate the civil rights movement in the United States when she refused to give up her seat to a white man on a Montgomery, Alabama bus in 1955. Her actions Rosa Parks (born February 4, 1913, Tuskegee, Alabama, U.S.—died October 24, 2005, Detroit, Michigan) was an American civil rights activist whose refusal to relinquish her seat on a public bus precipitated the 1955–56 Montgomery bus boycott in Alabama, which became the spark that ignited the civil rights movement in the United States. Accomplishments of Rosa Parks 1. Sparked the Montgomery Bus Boycott. On December 1st, 1955, Rosa Parks, an African American woman, refused to give up her bus seat to a white passenger in Montgomery, Alabama. Her act of defiance ignited the Montgomery Bus Boycott, a nonviolent protest that lasted for 381 days. Who was Rosa Parks? Rosa Louise McCauley was born in Tuskegee, Alabama, on February 4, 1913. She grew up in a world that constantly reminded her she was considered “less than” because of the color of her skin. Schools, water fountains, restaurants, and even sidewalks were divided by strict segregation laws known as “Jim Crow” laws. Parks, whose refusal to give up her bus seat to a white man sparked the modern civil rights movement, died of natural causes in her Detroit home on Monday, Oct. 24, 2005. She was 92-years-old. On 1 December 1955, Rosa Parks was arrested in Alabama for refusing to give up her bus seat to a white man. Discover how her act of defiance sparked the US civil rights movement. Rosa's early life experiences and involvement in civil rights activism laid the foundation for her historic act of defiance on December 1, 1955. Her refusal to give up her seat on a segregated bus sparked the Montgomery Bus Boycott, which would become a pivotal moment in the Civil Rights Movement. Rosa Parks may have been just one person, but Rosa Parks’ legacy is often simplified to her role in sparking the Montgomery Bus Boycott, but her lifelong commitment to justice went far beyond that single act of defiance. She understood that systemic oppression operates on multiple fronts —racial, gendered, and economic—and that true justice requires addressing all these dimensions. Rosa Parks (1913–2005) is best known for her refusal to give up her seat to a white man on a crowded bus in Montgomery, Alabama, on December 1, 1955. Her arrest sparked the Montgomery Bus Boycott, a pivotal event in the civil rights movement that ultimately led to the dismantling of Jim Crow segregation. Rosa Parks became an icon of the movement, celebrated for this single courageous act of Rosa parks is known for her positive deviance because: a. she was expected to sit in the from of the bus and sat in the back b. she was not allowed on the bus and got on anyway c. she was expected to sit in the back of the bus and sat in the back d. she was expected to sit in the back of the bus and sat in the front Rosa Parks is a pivotal figure in the African American civil rights movement, best known for her act of positive deviance on December 1, 1955, when she refused to give up her seat to a white man on a Montgomery, Alabama, bus. According to your textbook, on December 1, 1955, in Montgomery, Alabama, Rosa Parks refused to give up her bus seat. Her act of civil disobedience is considered an example of __________. Positive Deviance c. Deviance occurs whenever someone else is harmed by an action. d. Deviance is socially defined., During the civil rights movement, Rosa Parks and other black protestors spoke out against segregation by refusing to sit at the back of the bus. This is an example of _____. a. An act of social control b. An act of deviance c. A social norm d. Inderbitzin, Bates & Gainey, Deviance and Social Control 2nd Edition Instructor Resource 2 5. Rosa Parks is known for her act of positive deviance because: a) she was expected to sit in the back of the bus and chose to sit in the back. b) she was expected to sit in the back of the bus and refused to sit in the back. The means of enforcing rules are known as sanctions. Sanctions can be positive as well as negative.Positive sanctions are rewards given for conforming to norms. A promotion at work is a positive sanction for working hard.Negative sanctions are punishments for violating norms. Being arrested is a punishment for shoplifting. Rosa Parks The Hunger Games Positive and Negative Deviance Overview of the Hunger Games A popular Hollywood movie where every year the government in the Capitol organizes an event known as the Hunger Games: a bloody, gladiator-style fight-to-the-death battle between 24 Rosa Parks' act of refusing to move to the back of a public bus in Montgomery, Alabama is an example of secondary deviance in the context of the civil rights movement. Explanation: The subject of this question is History. Rosa Parks is best known for her refusal to move to the back of a public bus in Montgomery, Alabama on December 1, 1955. Promoting social change: Deviance can also encourage the dominant society to consider alternative norms and values. Rosa Parks’s act of deviance in Montgomery, Alabama, in 1955 led to the U.S. Supreme Court’s declaration that segregation on public transportation was unconstitutional. Strain Theory of Deviance During the civil rights movement, Rosa Parks and other black protestors spoke out against segregation by refusing to sit at the back of the bus. This is an example of _____. An act of social control; An act of deviance; A social norm; Criminal mores; Answer. B. A student has a habit of talking on her cell phone during class.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
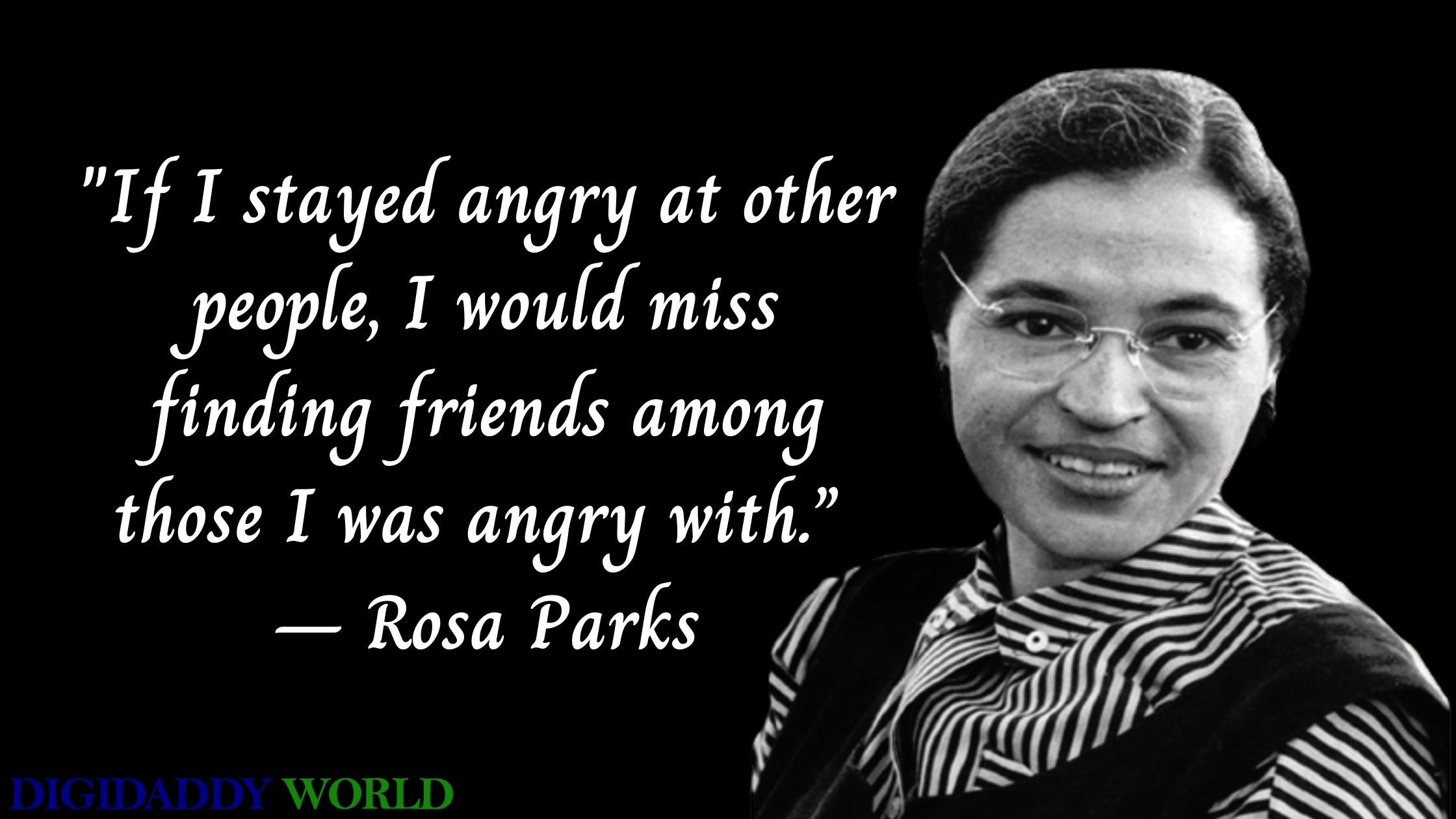 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |