Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
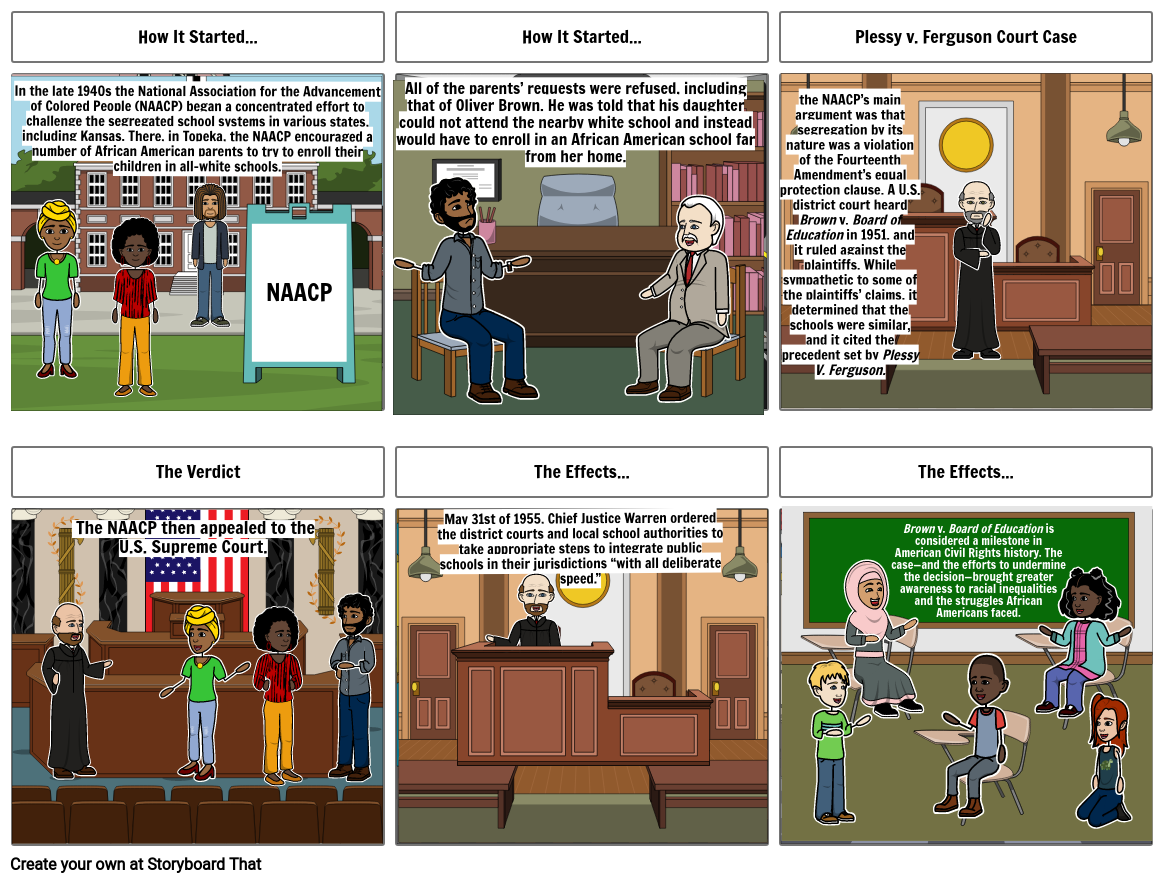
Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka was a landmark 1954 Supreme Court case in which the justices ruled unanimously that racial segregation of children in public schools was unconstitutional. On a cold day in the winter of 1955, Rosa Parks (1955), a college-educated 42-year-old black seamstress, refused to get up from her seat near the front of a Montgomery city bus to make way for a white man Brown v. Board of Education, case in which, on May 17, 1954, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled unanimously (9–0) that racial segregation in public schools was unconstitutional. It was one of the most important cases in the Court’s history, and it helped inspire the American civil rights movement of the late 1950s and ’60s. Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka, 347 U.S. 483 (1954), was a landmark decision of the United States Supreme Court, which declared that separate public schools for black and white students denied black children equal educational opportunities, paving the way for integration and the civil rights movement. Case history The NAACP’s long battle against de jure segregation culminated in the Supreme Court’s landmark Brown v. Board of Education decision, which overturned the “separate but equal” doctrine. Former NAACP Branch Secretary Rosa Parks’ refusal to yield her seat to a white man sparked the Montgomery Bus Boycott and the modern civil rights movement. EnlargeDownload Link Citation: Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka, Opinion; May 17, 1954; Records of the Supreme Court of the United States; Record Group 267; National Archives. View All Pages in the National Archives Catalog View Transcript In this milestone decision, the Supreme Court ruled that separating children in public schools on the basis of race was unconstitutional. It signaled On May 17, 1954, the Court stripped away constitutional sanctions for segregation by race, and made equal opportunity in education the law of the land. Brown v. Board of Education reached the Supreme Court through the fearless efforts of lawyers, community activists, parents, and students. Their struggle to fulfill the American dream set in More than five decades after Brown v. Board of Education, and 140 years after the enactment of the 14th Amendment, there is no doubt that deep racial disparities still persist. The Supreme Court has been systematically gutting the Brown decision over the past 57 years in ways that would make Thurgood Marshall and Constance Baker Motley weep. Impact of Brown v. Board of Education Though the Supreme Court’s decision in Brown v. Board didn’t achieve school desegregation on its own, the ruling (and the steadfast resistance to it across the South) fueled the nascent civil rights movement in the United States. In 1955, a year after the Brown v. Board of Education decision, Rosa Parks On May 17, 1954, a decision in the Brown v.Board of Education case declared the “separate but equal” doctrine unconstitutional. The landmark Brown v.Board decision gave LDF its most celebrated victory in a long, storied history of fighting for civil rights and marked a defining moment in US history. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Brown v. Board of Education Rosa Parks Little Rock Nine, Montgomery, Alabama, Recant and more. Three significant contributors to the rise of the civil rights movement include Rosa Parks' refusal to give up her bus seat, the landmark Supreme Court case Brown v. Board of Education which outlawed school segregation, and the actions of the Little Rock Nine who integrated a high school in Arkansas. The rise of the civil rights movement was due to the following . Rosa Parks . Brown v. Board of Education . Little Rock Nine . Who are these people . Rosa Parks: Rosa Parks, an African American woman, became a prominent figure in the civil rights movement after her refusal to give up her seat to a white passenger on a bus in Montgomery, Alabama, in 1955, Three key events that set off the civil rights movement during the 1950s include the Brown v. Board of Education ruling, Rosa Parks' bus boycott, and the Little Rock Nine's integration into Central High School. Each event challenged the status quo of segregation and spurred significant public action. The Supreme Court’s decision in Brown v. Board of Education paved the way for a new level of opportunity for others that followed by making segregation in schools illegal, providing better conditions in the classroom, and providing African American students with more opportunities for the future. In commemoration of the 70th anniversary of Brown v. Board of Education (1954), Matthew Delmont discusses the symbolic and practical significance of the landmark decision. Although it deemed legal segregation unconstitutional, Brown v. Board did not result in meaningful school integration right away. In fact, the decision represents the long Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Thurgood Marshall, Brown v Board of Education of Topeka, Rosa Parks and more. The reaction to Brown v. Board of Education was violent and many governors called out state militias to prevent rioting in the streets. met with massive resistance in the South as states argued that public education was beyond the jurisdiction of the federal government and they would refuse to comply. quiet acceptance in most of the South since the Supreme Court decision was unanimous and The Brown Foundation c/o 1817 Foxwood Ln • The Villages, Florida 32162 352-566-4920 • Contact Us The Brown Foundation c/o 1817 Foxwood Ln • The Villages, Florida 32162 352-566-4920 • Contact Us
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |